A gestão de ativos de TI (IT Asset Management) é uma prática estratégica essencial para empresas que buscam controle, eficiência e governança sobre seus recursos tecnológicos. Com o avanço das soluções em nuvem, a mobilidade e o aumento da complexidade dos ambientes de TI, adotar uma abordagem estruturada por meio de um ITAM software se tornou indispensável. ITAM não se trata apenas de inventariar equipamentos ou licenças, mas sim de garantir que cada ativo de TI — físico ou digital — esteja alinhado aos objetivos de negócio, gerando valor em todas as fases do seu ciclo de vida. Neste contexto, contar com ITAM soluções robustas permite reduzir riscos, melhorar a previsibilidade de investimentos e apoiar decisões mais inteligentes sobre aquisições, uso e descarte de ativos.
Através da implementação de uma estratégia efetiva de gestão de ativos de tecnologia da informação, as organizações têm a oportunidade de aprimorar sua eficácia operacional, elevar o nível de segurança e diminuir os gastos financeiros. Adicionalmente, a gestão de ativos de TI pode auxiliar as empresas a se manterem em conformidade com regulamentações, além de permitir que tomem decisões conscientes referentes à aquisição, manutenção e atualização de seus ativos tecnológicos. A gestão de ativos de TI representa um elemento fundamental no gerenciamento empresarial atual, capaz de otimizar o valor dos investimentos em tecnologia.
Tipos de Gestão de Ativos de TI
De maneira geral, os ativos de TI podem ser classificados em uma ou mais das seguintes categorias: físicos, de software, de hardware, de tecnologia móvel e de nuvem. O ITAM foi criado com o objetivo de garantir a implantação bem-sucedida e o suporte contínuo desses ativos.
Existem três tipos principais de gerenciamento de ativos de TI:
Software: este tipo de gerenciamento de ativos de TI é um pouco mais complexo do que os outros, pois envolve aspectos como requisitos de conformidade, licenciamento, shadow IT e IoT. Os ativos de software precisam ser monitorados e revisados continuamente, e devem ser flexíveis o suficiente para seguir os requisitos e atender às demandas de um mercado em constante mudança.
Hardware: o hardware físico também desempenha um papel fundamental no ecossistema de TI de uma organização. Esses ativos físicos incluem computadores, impressoras, copiadoras, notebooks, dispositivos móveis, servidores e qualquer outro hardware utilizado para gerenciamento de dados na empresa.
Nuvem: o ITAM monitora o custo e o uso dos recursos em nuvem, incluindo SaaS (Software como serviço), IaaS (Infraestrutura como serviço) e PaaS (Plataforma como serviço). Todos esses recursos são considerados ativos a serem gerenciados em termos de custo e conformidade no ITAM.
Padrões de ISO para IT Asset Management
A ISO (Organização Internacional de Normalização) criou uma família oficial de padrões para gerenciamento de ativos de TI, conhecida como ISO 19770, que consiste em cinco partes:
- ISO/IEC 19770-1: Descreve as práticas recomendadas para o gerenciamento de ativos de TI de uma empresa. As organizações podem utilizar este padrão para comprovar que estão seguindo as práticas recomendadas de gerenciamento de ativos de TI e atendendo aos requisitos de governança, oferecendo suporte às atividades de TI.
- ISO/IEC 19770-2: Ajuda as empresas a identificarem programas de software em dispositivos específicos, utilizando um padrão para identificação de software.
- ISO/IEC 19770-3: Detalha as atribuições associadas a um software e o método de medição de seu consumo.
- ISO/IEC 19770-4: Permite a geração de relatórios padronizados sobre o uso de recursos. Isso é particularmente importante ao gerenciar licenças de software mais complexas e software e hardware baseados em nuvem.
- ISO/IEC 19770-5: Fornece uma visão geral dos padrões e do vocabulário da ISO para gerenciamento de ativos de TI.
O ciclo de vida dos ativos de TI
O ciclo de vida dos ativos de TI é um dos pilares da gestão de ativos de TI eficaz. Ele abrange todas as etapas pelas quais um ativo passa: desde o planejamento e aquisição, passando pela implementação, monitoramento, manutenção, até chegar ao seu descarte ou substituição. Um ITAM software adequado permite mapear e controlar essas fases com precisão, promovendo transparência e governança. Esse processo evita aquisições desnecessárias, facilita auditorias e garante o uso eficiente dos recursos. Ao adotar ITAM soluções integradas ao ecossistema de TI, as empresas conseguem manter sua infraestrutura otimizada e em conformidade com políticas internas e regulamentações externas.
O gerenciamento dos ativos de TI segue um ciclo de vida que envolve diversas etapas, como o Solicitação, Execução, implantação, operação, manutenção e descarte. Cada uma dessas etapas é crucial para garantir que os ativos de TI sejam gerenciados de forma eficaz e atendam às necessidades da empresa.
A pri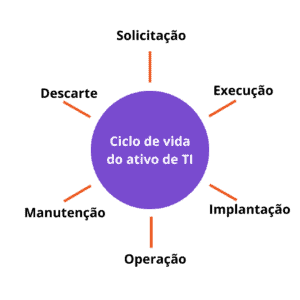
Na segunda etapa, ocorre a execução, onde os ativos de TI são comprados de fornecedores selecionados e negociados através de contratos de compra.
A terceira etapa é a implantação, onde ocorre a instalação e configuração dos ativos de TI adquiridos, podendo incluir a instalação de hardware, software e a configuração de redes.
A quarta etapa é a Operação, onde os ativos de TI são utilizados diariamente para fins comerciais, administrando servidores, oferecendo suporte técnico para usuários finais e mantendo uma rede estável e segura.
A quinta etapa é a Manutenção, onde a manutenção preventiva e corretiva é realizada para garantir que os ativos de TI continuem funcionando corretamente e estejam sempre atualizados, incluindo a instalação de patches de segurança, atualização de software e reparação de hardware danificado.
Por fim, a sexta etapa é a Descarte, onde ocorre a remoção segura dos ativos de TI no final de sua vida útil, incluindo a reciclagem ou descarte seguro de hardware e a remoção segura de dados sensíveis armazenados nos ativos de TI.
É importante ressaltar que, quando se trata de hardware, o “inventário” pode ser incluído como uma fase separada para garantir o controle e gerenciamento adequado dos ativos de TI. O sucesso na conclusão deste ciclo de vida é fundamental para o gerenciamento eficaz dos ativos de TI de uma empresa e para garantir que eles sejam usados de forma segura e eficiente.
Check-in/check-out de equipamentos
Manter um controle adequado de equipamentos vitais é essencial para o gerenciamento eficiente dos ativos. Para isso, é importante ter um sistema centralizado e detalhado para o rastreamento e gerenciamento dos equipamentos. Esse sistema deve permitir que usuários autorizados solicitem empréstimos de ativos e incluir campos que identifiquem informações importantes, como a pessoa responsável pelo ativo, o local para onde ele será fornecido, o modelo do ativo, o período de uso previsto e a justificativa para a necessidade do ativo. Ter um sistema de rastreamento e gerenciamento de equipamentos vitais ajuda a garantir que os ativos sejam utilizados de forma adequada e eficiente.
Saber quem tem o quê
A efetiva gestão de empréstimo de equipamentos é importante para assegurar a contabilidade de todos os ativos e ter clareza sobre quem está usando o que e por quanto tempo. No entanto, a detecção de ativos pode fornecer informações adicionais sobre os dispositivos que uma empresa possui, além do que se espera, como suas configurações e os usuários que os utilizam. A detecção e a gestão de inventário devem ser realizadas em conjunto, com a implementação de automação para que todas as informações relevantes sejam inseridas automaticamente em um banco de dados, facilitando a revisão.
Rastreamento da localização dos ativos
Compreender quem está com os ativos, bem como sua disponibilidade, é crucial para o gerenciamento efetivo dos ativos de TI. No entanto, saber onde eles estão localizados é igualmente importante. O uso de tecnologias como RFID, GPS ou leitura de códigos de barras para rastrear a localização dos ativos pode ajudar a garantir que eles estejam no local certo. Além disso, caso um ativo seja considerado ausente, os rastreadores de localização podem ser inestimáveis para localizá-lo e protegê-lo.
Um repositório de ITAM
O repositório de ITAM é fundamental para armazenar e gerenciar dados financeiros, físicos e contratuais de ativos de TI. No entanto, um repositório eficaz não deve apenas servir como um local de armazenamento, mas também deve ser capaz de executar tarefas relacionadas ao gerenciamento de ativos de TI. É importante que o repositório esteja integrado a outras ferramentas de gerenciamento, como inventário, uso de software, suporte de serviço de TI, gerenciamento de mudanças, gerenciamento de configurações e compras. Essa integração permite que o repositório seja atualizado automaticamente com informações precisas e atualizadas, tornando mais fácil o gerenciamento e tomada de decisões relacionadas aos ativos de TI.
Informações de uso e inventário de hardware e software
Um gerenciamento bem-sucedido de ativos de TI está diretamente ligado à capacidade de acompanhar métricas relevantes. É fundamental identificar quais KPIs são prioritários para garantir o rastreamento das métricas corretas. Dessa forma, é possível melhorar o desempenho dos ativos, reduzir custos de manutenção e reparo, além de assegurar o uso e a efetividade ideais dos ativos. Há diversas métricas comuns que podem ser rastreadas, tais como:
- Custos
- Número de ativos
- Software licenciado/não licenciado
- Licenças utilizadas de modo insuficiente/em excesso
- Garantias expiradas
- Importação de dados
Para garantir o sucesso do ITAM, é fundamental contar com dados precisos e atualizados sobre os ativos, os quais podem ser provenientes de diversas fontes, como bancos de dados, servidores, plataformas e soluções. É essencial que esses dados sejam importados para um local centralizado, pois essa é uma etapa crucial para apresentar uma imagem fiel do patrimônio de ativos.
Benefícios do ITAM bem estruturado
Organizações que implementaram práticas maduras de IT Asset Management registram benefícios concretos e mensuráveis. Segundo a Gartner, empresas que adotam ITAM conseguem reduzir até 30% dos custos com software em seu primeiro ano de implementação. Em um estudo de caso conduzido pela ServiceNow, uma companhia global de manufatura economizou mais de US$ 4 milhões ao identificar e eliminar licenças de software subutilizadas. Além disso, o uso de ITAM software contribui diretamente para a conformidade regulatória, reduzindo riscos relacionados a auditorias e penalidades. Ao investir em ITAM soluções, as empresas não apenas controlam seus ativos, mas transformam sua área de TI em um verdadeiro centro de eficiência operacional e valor estratégico.
SAM (Software Asset Management)
SAM (Software Asset Management) ou Gestão de Ativos de Software é um conjunto de práticas e processos que ajudam as empresas a gerenciar e otimizar seus ativos de software. O SAM é importante porque o uso indevido de software pode levar a problemas legais e financeiros para as empresas.
A Gestão de Ativos de Software envolve a identificação de todos os softwares utilizados pela empresa, bem como a gestão das licenças para garantir que a empresa esteja em conformidade com as leis de propriedade intelectual. O objetivo final do SAM é garantir que a empresa esteja usando seus ativos de software de forma eficiente e econômica.
O Software Asset Management é importante para empresas de todos os tamanhos, mas é especialmente crítico para grandes empresas com muitos funcionários e sistemas complexos. O SAM pode ajudar a garantir que as empresas não estejam comprando mais licenças de software do que precisam e que estejam utilizando os softwares de forma adequada e eficiente.
HAM (Hardware Asset Management)
Hardware Asset Management (HAM) ou Gestão de Ativos de Hardware é um conjunto de práticas e processos que ajudam as empresas a gerenciar e otimizar seus ativos físicos. O HAM é importante porque o uso inadequado ou ineficiente de hardware pode levar a problemas financeiros e de segurança para as empresas.
O HAM envolve a identificação e o registro de todos os ativos de hardware da empresa, bem como a gestão desses ativos ao longo do ciclo de vida, desde aquisição até descarte. Seu objetivo final é garantir que a empresa esteja usando seus ativos de hardware de forma eficiente e econômica, maximizando a produtividade e minimizando os custos.
O Hardware Asset Management é especialmente importante para empresas que possuem grandes quantidades de ativos de físicos, incluindo desktops, laptops, servidores e dispositivos móveis. Com o HAM, as empresas podem monitorar e controlar o uso desses ativos, garantindo que eles estejam sendo usados apropriadamente e que não sejam desperdiçados.
Gerenciamento de recursos de nuvem (Cloud Insights)
SaaS
O gerenciamento de SaaS (Software as a Service) é o processo de supervisão e administração das aplicações SaaS utilizadas por uma organização. Para alcançar uma gestão eficaz, é necessário avaliar as necessidades de negócios e selecionar fornecedores de SaaS adequados, implantar aplicativos, integrar sistemas, gerenciar dados e segurança, gerenciar contas de usuários e monitorar o desempenho.
A gestão eficaz de SaaS pode ajudar as empresas a maximizar o valor dos aplicativos que utilizam, garantindo que eles atendam às necessidades de negócios e sejam utilizados de forma otimizada. Isso pode incluir a realização de avaliações regulares de uso e custo-benefício, seleção cuidadosa de fornecedores de SaaS, integração de sistemas para garantir interoperabilidade e automação de tarefas rotineiras.
A segurança é uma consideração importante no gerenciamento de SaaS, pois muitos aplicativos SaaS armazenam dados importantes da empresa na nuvem. É necessário garantir a segurança dos aplicativos SaaS e proteger os dados da empresa contra acesso não autorizado ou violações de segurança. Isso pode incluir a implementação de políticas de segurança de dados, como autenticação multifator, criptografia de dados, backups regulares e monitoramento de atividades suspeitas.
Outro aspecto crítico do gerenciamento de SaaS é a gestão de contas de usuários. Isso envolve o controle de acesso aos aplicativos SaaS, adição ou remoção de usuários, monitoramento de uso e análise de tendências para garantir que os usuários estejam obtendo o máximo valor dos aplicativos SaaS que utilizam.
Por fim, o gerenciamento de SaaS também inclui o monitoramento do desempenho dos aplicativos SaaS. Isso inclui a medição da disponibilidade e do tempo de atividade dos aplicativos, bem como a análise de desempenho para identificar gargalos e oportunidades de melhoria.
IaaS
O modelo de Infraestrutura como Serviço (IaaS) refere-se à hospedagem de recursos de computação em um ambiente de nuvem em vez de em um data center tradicional. O gerenciamento eficaz de IaaS envolve a monitorização do uso dos recursos computacionais disponíveis na nuvem, como capacidade de armazenamento e poder de processamento. Isso inclui a capacidade de escalar verticalmente, adicionando ou removendo recursos de acordo com as necessidades da organização, bem como a capacidade de monitorar o uso para identificar tendências e prever as necessidades futuras. O gerenciamento de IaaS também pode envolver a implementação de políticas de segurança para proteger os dados e as aplicações hospedadas na nuvem, bem como a monitorização do desempenho para garantir que os recursos estejam sendo usados de maneira eficaz e eficiente.
PaaS
Plataforma como serviço é um modelo de computação em nuvem que fornece um ambiente de desenvolvimento e implantação na nuvem para a construção de aplicativos. Ele permite que os desenvolvedores criem e implantem aplicativos sem a necessidade de gerenciar a infraestrutura subjacente. O gerenciamento de PaaS inclui a seleção cuidadosa de um provedor de PaaS, a compra de recursos conforme necessário e o monitoramento do uso para garantir a conformidade com o orçamento e o contrato de uso. O gerenciamento também pode incluir a implantação e configuração de aplicativos, a integração com outros serviços em nuvem e a monitoramento de desempenho para garantir que os aplicativos estejam funcionando corretamente. Além disso, o gerenciamento de PaaS também pode envolver a implementação de políticas de segurança para garantir que os dados do aplicativo e do cliente estejam protegidos contra ameaças externas.
Benefícios do gerenciamento de ativos de TI
Apresenta uma única fonte
O gerenciamento de ativos de TI busca criar um ambiente organizado e eficiente. Geralmente, os ativos de TI são monitorados e rastreados em várias fontes diferentes, sem um proprietário claro ou uma ferramenta centralizada para consolidar todas as informações. O ITAM ajuda a resolver esse problema, fornecendo um sistema que consolida os dados dos ativos, elimina a necessidade de rastrear artefatos manualmente, monitora o uso e interpreta as dependências dos ativos de forma mais eficiente. Isso resulta em um ambiente mais organizado e eficiente, permitindo que as empresas gerenciem seus ativos de TI com mais facilidade e eficácia.
Melhora a utilização, reduz os riscos e diminui o desperdício
Com o gerenciamento de ativos, as informações são atualizadas regularmente, permitindo que as equipes identifiquem e eliminem ativos desnecessários ou subutilizados, o que pode levar a uma utilização mais eficiente dos recursos e, portanto, reduzir o desperdício. Além disso, o controle dos ativos ajuda a garantir que os requisitos de segurança e conformidade sejam atendidos, reduzindo o risco de penalidades regulatórias associadas a violações de segurança ou não conformidade.
Aumenta a produtividade sem perder confiabilidade
À medida que as equipes de tecnologia adotam os princípios de DevOps e SRE, as ferramentas de gerenciamento de ativos se tornam cada vez mais importantes. Com uma maior dependência dos serviços de infraestrutura e plataforma, é crucial um gerenciamento eficaz de ativos, permitindo um melhor gerenciamento do consumo e utilização dos recursos.
Dá suporte às práticas de negócios e de TI e capacita as equipes
O gerenciamento de ativos oferece suporte a processos de ITSM e ITIL, incluindo gerenciamento de mudanças, incidentes e problemas. Com informações precisas prontamente disponíveis, as equipes podem se mover mais rapidamente e prever melhor os impactos antes que ocorram. Essa abordagem também é útil para departamentos de RH para integração e desligamento, finanças para rastreamento de ativos, segurança para correção de vulnerabilidades e gerenciamento de operações para descobrir ativos críticos e suas dependências.
Reduz os custos por meio de análises constantes
A análise constante e a consolidação dos ativos podem fornecer informações valiosas sobre o consumo de recursos, incluindo licenças, instâncias e outros recursos que podem estar sendo subutilizados ou usados em excesso. Essa prática ajuda a identificar se os recursos estão consumindo mais dinheiro do que o necessário e permite tomar decisões informadas sobre a redução de custos e o aumento da eficiência operacional.
O que é um banco de dados de IT Asset Management?
Os três componentes
No componente físico, as informações são frequentemente coletadas por meio de processos manuais, como a utilização de leitores de códigos de barras ou sistemas de RFID. Este método de coleta de dados visa identificar o que está implantado, o que pode estar em estoque e o que está programado para ser desativado.
Já o componente financeiro do banco de dados de ITAM é geralmente obtido de sistemas ou ordens de compra. Ele indica o número da ordem de compra, a quantidade, a marca e o modelo, a depreciação, o nome do fornecedor e o centro de custos. A coleta e rastreamento dessas informações são essenciais para oferecer dados precisos sobre o custo total de propriedade, o ROI e os orçamentos atribuídos a projetos e serviços.
Por fim, o componente contratual é composto pelos dados coletados de revendedores, fornecedores ou sistemas de gerenciamento de contratos. As informações incluem a versão final de um contrato, atribuição de licenças, número de dispositivos, preço de compra, SKU do fornecedor, níveis de serviço e manutenção. Tais informações são importantes para gerenciamento de contratos e auxiliam na tomada de decisões sobre aquisições e renovações.
Práticas recomendadas do IT Asset Management
- Comece com a adesão executiva
- Inicie uma equipe para fazer o piloto do projeto
- Defina os ativos essenciais
- Identifique os recursos de nuvem
- Determine métodos para detecção e integração de dados
- Use uma abordagem baseada no ciclo de vida
- Seja proativo em suas iniciativas de rastreamento e acompanhe-as continuamente para evitar o excesso de implantação
- Decida se deseja usar um CMDB
- Automatize o máximo possível
- Integre e disponibilize dados para toda TI
- Conheça suas licenças de software
- Reúna feedback para melhorias contínuas
- Envolva outras equipes no feedback
Como saber se ITAM Soluções são ideais para minha organização?
Existem vários motivos pelos quais o ITAM pode apoiar sua organização, como por exemplo:
Você quer economizar dinheiro?
Otimizar os gastos com software, infraestrutura e serviços de plataforma é uma estratégia essencial para reduzir custos. Ao adotar as práticas recomendadas para a otimização de licenças de software e uso de ativos, as organizações podem obter uma redução de até 30% nos gastos.
Você depende de planilhas?
Ainda hoje, muitas empresas dependem de planilhas para rastrear seus ativos, no entanto, essas planilhas não são completamente precisas. Além disso, elas criam silos de dados que dificultam o acesso de todos os usuários autorizados às mesmas informações atualizadas.
É difícil acompanhar o ritmo das mudanças?
O rastreamento de ativos de TI pode se tornar uma tarefa difícil, já que esses ativos estão em constante movimento. Gerenciar problemas como perda, substituição, desativação e recebimento de novos ativos pode ser bastante caótico, exigindo muita atenção aos detalhes.
O shadow IT é uma realidade
Shadow IT se refere a aplicativos, licenças e outros ativos de TI que estão sendo adquiridos e usados sem o conhecimento da equipe de TI. O software centralizado de ITAM mantém a TI a par de tudo e evita gastos excessivos, riscos e não conformidade. A shadow IT é uma realidade que quase todas as empresas modernas enfrentam. Como você a gerencia fará diferença no nível de controle necessário para reduzir riscos e gastos.
Gostaria de saber mais sobre como implementar um sistema de ITAM eficaz para sua empresa? Entre em contato conosco agora mesmo para falar com um especialista em gerenciamento de ativos de TI e descobrir como podemos ajudá-lo a reduzir custos, melhorar a eficiência operacional e maximizar o retorno sobre o investimento em tecnologia. Clique para falar com um especialista.


