Ter consciência de que a Tecnologia da Informação (TI) é uma área estratégica para as companhias não basta para que elas atinjam um desempenho mais expressivo. Também é imprescindível que as empresas adotem boas práticas de gestão para que os serviços ligados a esse segmento estejam dentro ou acima das expectativas. Esse cenário fortalece a necessidade de apostar na metodologia ITIL.
Atualmente, ela é uma das mais requisitadas pelos gestores de TI, porque serve de base sobre como administrar as tarefas de uma equipe e manter as atividades sendo executadas de forma exemplar.
Neste artigo, vamos abordar diversos pontos sobre esse método de gerenciar serviços de TI, com o objetivo de você adotá-lo no seu negócio com eficiência. Confira!
Visão Geral do ITIL: História, Evolução e Importância
O Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) surgiu como um conjunto de melhores práticas para a gestão de serviços de TI, evoluindo ao longo do tempo para se adaptar às necessidades do mercado. Desde as suas primeiras versões até ao ITIL 4, a estrutura passou por transformações significativas, incorporando conceitos modernos de ITSM (Gestão de Serviços de Tecnologia da Informação) e enfatizando princípios orientadores como foco no valor, pensar e trabalhar holisticamente, e manter a simplicidade e a praticidade.
Para as empresas, adotar o ITIL significa alinhar a TI com os objetivos de negócio, melhorar a eficiência operacional, aumentar a satisfação do cliente e, em última análise, agregar mais valor aos serviços prestados.
Qual a melhor resposta sobre o que é ITIL?
Com certeza, uma boa maneira de definir essa metodologia de gestão de TI é afirmar que se trata de uma biblioteca com as práticas mais indicadas para administrar os serviços de Tecnologia da Informação.
Também é comum denominar ITIL como uma biblioteca, ou seja, um conjunto de obras em que estão documentadas as ações mais bem-sucedidas ao redor do mundo sobre o gerenciamento de TI, após décadas de aquisição de conhecimento.
Vale destacar que o significado da sigla ITIL é: Information Technology Infrastructure Library. Em português, significa Biblioteca de Infraestrutura de Tecnologia da Informação.
Contudo, ITIL não se refere especificamente à infraestrutura de TI. O foco é uma abordagem ampla sobre a gestão tecnológica, o que abrange também atividades ligadas ao desenvolvimento de softwares.
Com o surgimento de uma base de informações relacionadas com a governança de TI e o gerenciamento de serviços tecnológicos, essa metodologia passou a reunir uma gama maior de conhecimento, aspecto imprescindível para agregar valor aos trabalhos dos gestores de Tecnologia da Informação.
Entenda o conceito ITIL V3
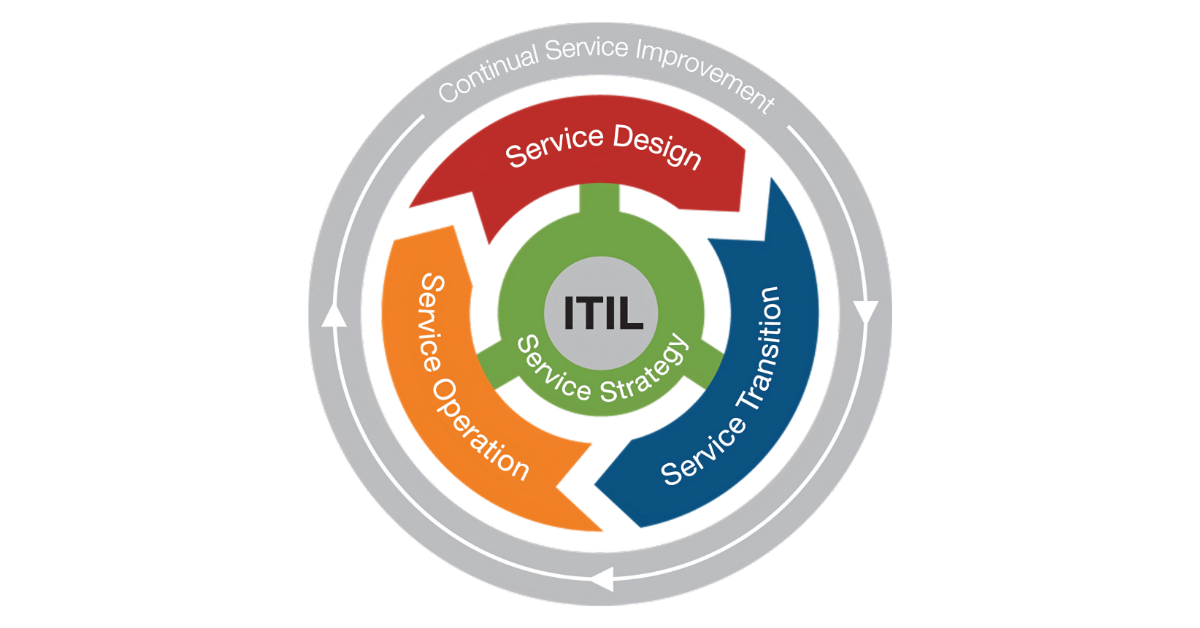
Para implementar o método ITIL de gestão de TI, recomendamos conhecer as modalidades que uma empresa pode implementar. Uma delas é o ITIL V3, que adotamos a partir de 2011.
Nele, o ciclo de vida das atividades divide-se em cinco princípios: serviço, processos, funções, medidas e desempenho. Para que você assimile isso de forma plena, abordaremos os estágios mais relevantes na adoção do ITIL V3. Acompanhe!
Estratégia
A meta estabelece a estratégia para uma empresa oferecer serviços digitais aos clientes e manter as atividades funcionando de forma adequada. Para isso, focamos também na implementação de uma cultura voltada para ações direcionadas aos resultados mais impactantes.
Desenho
Nesse momento, transformamos a estratégia de serviço em atividades concretas. Realizamos isso por meio do lançamento de novos serviços ou do aprimoramento dos já oferecidos atualmente.
Transição
A intenção reúne todos os ativos de um serviço para realizar testes e integrá-los. Esse trabalho verifica a qualidade de um novo serviço para que ele seja lançado de acordo com as melhores práticas do mercado.
Operação
Essa etapa prioriza a adoção de iniciativas que viabilizam a oferta de serviços responsivos. Para concretizar isso, estruturamos a gestão de incidentes e a central de atendimentos, o que colabora para que uma empresa seja mais dinâmica na manutenção das atividades.
Melhoria Contínua
Os trabalhos voltam-se para expandir a eficácia e a eficiência dos processos e atividades de TI em uma corporação. Esse estágio visa fazer com que as práticas das demais fases busquem alternativas para melhorar continuamente.
Conheça o ITIL 4
Consiste na versão mais atualizada da metodologia ITIL, sendo lançada em fevereiro de 2019. Vale mencionar que houve profundas mudanças na arquitetura do método.
Com a intenção de expor isso de maneira mais clara, vamos mostrar como o ITIL 4 está composto. Por isso, é importante ler este conteúdo com bastante atenção!
Organizações e pessoas
Por mais que os serviços de TI envolvam software e hardware, é impossível ignorar a relevância dos clientes (internos ou externos), fornecedores e da equipe de Tecnologia da Informação.
Por isso, é muito importante haver um foco em como a gestão dos serviços pode proporcionar uma boa experiência para os stakeholders a partir da melhoria contínua dos trabalhos.
Informação e Tecnologia
As atividades estão voltadas para o gerenciamento do setor de TI promover uma maior disponibilidade dos sistemas e dos serviços digitais, com foco em segurança da informação.
Parceiros e fornecedores
Para superar os desafios da transformação digital, a área de Tecnologia da Informação necessita de parcerias e de fornecedores de alto nível. Esse fator favorece a contratação de consultorias, equipamentos, software houses e até de fábrica de software.
Fluxos de valor e processos
Nessa fase, o olhar é voltado para os processos de TI. Assim, são maiores as possibilidades de aprimorá-los, levando em consideração as necessidades dos clientes. Essa postura mostra um comportamento mais proativo diante das transformações do mercado.
É válido afirmar que esses quatro estágios do ITIL 4 podem sofrer influências econômicas, ambientais, legais, políticas e tecnológicas. Além disso, essa nova versão se caracteriza por dar um maior foco nos stakeholders em vez da estruturação do serviço em si.
As 34 Práticas do ITIL 4
O ITIL 4 detalha 34 práticas distintas, essenciais para uma gestão de serviços de TI eficaz. Estas práticas são agrupadas em três categorias principais: gestão geral, que engloba aspetos estratégicos e de planeamento; gestão de serviços, focada na entrega e suporte dos serviços; e gestão técnica, que lida com aspetos tecnológicos específicos. A compreensão e implementação destas práticas são cruciais para as organizações que buscam otimizar os seus processos de ITSM e garantir a qualidade e a confiabilidade dos seus serviços de TI. Veja de maneira simplória quais são as 34 práticas do framework ITIL 4:
Geral:
- Arquitetura de Gestão: Fornece uma compreensão de todos os componentes de uma organização e como eles se encaixam, auxiliando no planeamento e na tomada de decisões.
- Melhoria Contínua: Estabelece uma cultura de melhoria em toda a organização e em todos os seus serviços e práticas.
- Informação e Conhecimento: Gere a informação e o conhecimento necessários para apoiar todas as práticas de gestão de serviços.
- Medição e Relato: Apoia a tomada de decisões e a melhoria contínua, fornecendo visibilidade sobre o desempenho dos serviços e da organização.
- Riscos: Garante que a organização avalie e gerencie os riscos de forma eficaz.
- Segurança da Informação: Protege a informação necessária para fornecer e dar suporte aos serviços.
- Projetos: Garante que todos os projetos da organização sejam geridos com sucesso.
- Relacionamento: Estabelece e mantém relacionamentos entre a organização e as suas partes interessadas em todos os níveis estratégicos e táticos.
- Estratégica: Formula os objetivos da organização e adota os cursos de ação necessários para atingi-los.
- Fornecedores: Garante que os fornecedores da organização e os seus desempenhos sejam geridos de forma adequada para apoiar a prestação de serviços contínuos e de qualidade.
- Recursos Humanos: Garante que a organização tenha as pessoas certas com as habilidades e competências necessárias.
Serviços:
- Análise de Negócios: Analisa as necessidades de negócio e identifica as soluções possíveis para satisfazê-las.
- Catálogo de Serviços: Fornece uma única fonte de informação consistente sobre todos os serviços e ofertas de serviço da organização.
- Capacidade e Desempenho: Garante que os serviços tenham a capacidade e o desempenho necessários para atender à demanda acordada.
- Continuidade do Serviço: Garante que os serviços possam continuar a ser entregues dentro de níveis de serviço acordados após uma interrupção.
- Monitoramento e Gestão de Eventos: Observa sistematicamente os serviços e os componentes do serviço e gere e prioriza as notificações de mudança de estado (eventos).
- Incidentes: Minimiza o impacto negativo dos incidentes, restaurando o serviço normal o mais rapidamente possível.
- Problemas: Reduz a probabilidade e o impacto dos incidentes, identificando as causas reais e desenvolvendo soluções.
- Liberação: Disponibiliza serviços novos e alterados para uso.
- Controle de Mudanças: Maximize o número de mudanças de TI bem-sucedidas, garantindo que os riscos sejam adequadamente avaliados, autorizados e geridos.
- Validação e Teste de Serviços: Garante que os serviços novos e alterados atendam às expectativas acordadas.
- Nível de Serviço: Define as metas para o desempenho do serviço e mede, monitora e relata o desempenho real em relação a essas metas.
- Requisições de Serviço: Apoia o manuseio de todas as solicitações de serviço predefinidas e iniciadas pelo utilizador de forma eficaz e amigável.
Técnica:
- Implantação: Move componentes de serviço novos ou alterados para ambientes ativos.
- Infraestrutura e Plataforma: Supervisiona e gere os ambientes de hardware e software necessários para dar suporte aos serviços.
- Desenvolvimento e Gestão de Software: Cria e gere o software necessário para fornecer e dar suporte aos serviços.
Avalie como implementar essa metodologia
Além do foco na melhoria contínua dos processos e serviços, é necessário ter um olhar atento nos colaboradores para o ITIL se tornar uma prática real no cotidiano de uma empresa.
A partir do conhecimento das versões mais empregadas do método, é possível pensar nos passos necessários para a implementação. Contudo, deve haver uma prioridade na qualificação da equipe para boas práticas de TI serem efetivadas de forma plena.
Esse cenário faz com que as companhias tenham um foco em incentivar os funcionários a obter o ITIL Foundation, certificação necessária para seguir os melhores procedimentos de gestão de Tecnologia da Informação.
Atualmente, a certificação ITIL 4 Foundation é uma porta de entrada para a adoção da versão mais atualizada do framework ITIL. Isso porque permite um conhecimento de como o gerenciamento de TI envolve a criação, entrega e evolução contínua dos serviços.
Para os profissionais de TI, essa certificação ajuda a compreender a estrutura ITIL e como ela pode ser útil no aperfeiçoamento da administração dos serviços de Tecnologia da Informação.
À medida que uma companhia conta com profissionais devidamente habilitados, mais rápida e simples será a implementação da metodologia ITIL em curto prazo.
Veja algumas vantagens de adotar ITIL na sua empresa
Há diversos benefícios em empregar um método de trabalho com foco na melhoria contínua dos serviços de TI. E entender isso, sem dúvida, vai te ajudar a compreender como investir em uma metodologia avançada de gestão pode fazer a diferença.
Uma vantagem significativa do ITIL envolve a clareza e a rapidez ao priorizar as demandas. Ao executar isso corretamente, a equipe terá um direcionamento do que precisa ser feito de forma mais ágil. Isso contribui para o aumento da produtividade e o foco em resultados.
Com uma equipe mais bem estruturada, também é viável reduzir os custos e os riscos de TI. Se as empresas adotarem boas práticas de monitoramento e prevenção a ataques cibernéticos, terão consequentemente menos gastos com manutenção. Além disso, isso minimizará as probabilidades de prejuízos com paralisações imprevistas nos serviços.
Outro benefício marcante da metodologia ITIL é fazer com que o setor de TI esteja mais alinhado com a estratégia de negócio. Isso porque a equipe de Tecnologia da Informação vai atuar de acordo com os principais objetivos da organização, o que é crucial para a evolução permanente dos serviços.
Há muitos fatores que justificam um investimento em ITIL. Afinal, é preciso fazer com que o gerenciamento das atividades de TI esteja dentro das perspectivas e das necessidades institucionais.
Histórico
Respondendo à crescente dependência de TI, a Agência Central de Computação e Telecomunicações (CCTA) do Governo do Reino Unido, na década de 1980, desenvolveu um conjunto de recomendações. Reconheceu que, sem padrões, as agências governamentais e os contratos do setor privado começaram a criar independentemente suas próprias práticas de gerenciamento de TI.
A Biblioteca de Infraestrutura de TI originou-se como uma coleção de livros, cada um abrangendo uma prática específica dentro do gerenciamento de serviços de TI. O ITIL foi construído em torno de uma visão baseada em modelo de processo de controlar e gerenciar operações frequentemente creditadas a W. Edwards Deming e seu ciclo PDCA (planejar-fazer-checar-agir).
Linha do tempo do ITIL
Após a publicação inicial em 1989-96, o número de livros cresceu rapidamente dentro da versão 1 do ITIL para mais de 30 volumes.
Em 2000/2001, para tornar o ITIL mais acessível (e acessível), o ITIL Versão 2 consolidou as publicações em nove “conjuntos” lógicos que agrupavam as diretrizes de processo relacionadas para corresponder a diferentes aspectos do gerenciamento de TI, aplicativos e serviços.
-
Os conjuntos de Gerenciamento de Serviço (Suporte de Serviço e Entrega de Serviço) eram, de longe, os mais amplamente usados, divulgados e compreendidos das publicações do ITIL Versão 2.
-
Em abril de 2001, o OGC, um escritório do Tesouro do Reino Unido, incorporou a CCTA.
-
Em 2006, publicaram o glossário do ITIL Versão 2.
-
Em maio de 2007, esta organização emitiu o ITIL versão 3 (também conhecido como o ITIL Refresh Project), que compunha-se de 26 processos e funções, agora agrupados em apenas 5 volumes, organizados em torno do conceito de estrutura de ciclo de vida do serviço. Agora, conhecemos a versão 3 do ITIL como ITIL 2007 Edition.
-
Em 2009, o OGC anunciou oficialmente que a certificação da ITIL Versão 2 seria retirada e lançou uma consulta importante sobre como proceder.
-
Em julho de 2011, publicaram a edição de 2011 do ITIL, que forneceu uma atualização para a versão publicada em 2007. Após a consolidação do OGC no Gabinete, o OGC não é mais listado como o proprietário do ITIL.
A 4ª edição do ITIL começa com o livro ITIL Foundation, lançado em 18 de fevereiro de 2019.
A Jornada Contínua do ITIL na Era da Transformação Digital
A evolução do ITIL, desde sua concepção pela Agência Central de Computadores, reflete a necessidade constante de adaptação às mudanças no cenário de TI. A versão atual, ITIL v4, representa um marco na forma como as organizações abordam o gerenciamento de serviços de TI, especialmente no contexto da transformação digital.
Implementando o ITIL com Sucesso
A implementação do ITIL exige um plano de ação bem definido, que considere as particularidades de cada organização. Para garantir o sucesso, é essencial:
1º Passo:
- Compreender os princípios orientadores: Os princípios orientadores do ITIL 4 servem como base para todas as decisões e ações, garantindo que os serviços de TI estejam alinhados com os objetivos estratégicos da empresa.
- Definir os processos de TI: Identificar e documentar quais são os processos de TI existentes e como eles se relacionam entre si é fundamental para otimizar o fluxo de trabalho e garantir a eficiência operacional.
- Investir em certificação ITIL: A certificação ITIL, especialmente a ITIL4 Foundation, é essencial para garantir que os profissionais de TI estejam familiarizados com as melhores práticas e possam aplicá-las de forma eficaz.
- Promover a melhoria contínua: O continual service improvement é um elemento chave do ITIL, incentivando as organizações a buscar constantemente maneiras de aprimorar seus serviços e processos.
- Gerenciar os riscos: O gerenciamento de riscos é crucial para garantir a segurança da informação e a continuidade dos serviços de TI.
2º Passo:
- Gerenciar as mudanças: O gerenciamento de mudanças é uma prática essencial para garantir que as alterações na infraestrutura de tecnologia sejam implementadas de forma controlada e eficiente.
- Gerenciar os incidentes: O gerenciamento de incidente é fundamental para garantir a rápida restauração dos serviços de TI em caso de interrupções.
- Gerenciar a configuração: O gerenciamento de configuração é essencial para garantir que os componentes da infraestrutura de TI sejam identificados, controlados e monitorados.
- Gerenciar a disponibilidade: O gerenciamento de disponibilidade é crucial para garantir que os serviços de TI estejam disponíveis quando necessário.
- Gerenciar as liberações: O gerenciamento de liberação é essencial para garantir que as novas versões de software e hardware sejam implementadas de forma controlada e eficiente.
3º Passo:
- Gerenciar os portfólios: O gerenciamento de portfólios é fundamental para garantir que os investimentos em TI estejam alinhados com os objetivos estratégicos da empresa.
- Adotar as práticas de gerenciamento: A implementação das práticas de gerenciamento do ITIL, incluindo as práticas gerais e as práticas de gerenciamento técnico, é essencial para garantir a qualidade e a eficiência dos serviços de TI.
- Alinhar com os objetivos: O alinhamento com os objetivos da empresa é fundamental para garantir que os serviços de TI agreguem valor ao negócio.
- Atender as demandas: O atendimento ao cliente e a satisfação do cliente são prioridades no ITIL 4, que busca garantir que os serviços de TI atendam às demandas dos usuários.
Benefícios da Implementação do ITIL
A adoção do ITIL traz diversos benefícios para as organizações, incluindo:
- Melhoria na qualidade dos serviços de TI: As melhores práticas do ITIL garantem que os serviços de TI sejam entregues de forma consistente e eficiente.
- Redução de custos: A otimização dos processos de TI e o gerenciamento de riscos contribuem para a redução de custos operacionais.
- Aumento da satisfação do cliente: O foco na experiência do cliente e no atendimento ao cliente garante que os usuários estejam satisfeitos com os serviços de TI.
- Alinhamento com os objetivos de negócios: O ITIL garante que os serviços de TI estejam alinhados com os objetivos estratégicos da empresa, contribuindo para o sucesso do negócio.
- Melhoria na comunicação e colaboração: O ITIL facilita a comunicação e a colaboração entre os profissionais de TI e as demais partes interessadas.
- Maior agilidade e adaptabilidade: O ITIL permite que as organizações se adaptem rapidamente às mudanças no mercado e nas necessidades dos clientes.
- Maior segurança da informação: O gerenciamento de riscos e a implementação de práticas de gerenciamento de segurança garantem a proteção dos dados e sistemas da empresa.
- Otimização da infraestrutura de tecnologia: O ITIL contribui para a otimização da infraestrutura de tecnologia, garantindo que os recursos sejam utilizados de forma eficiente.
- Melhora na tomada de decisões: O ITIL fornece informações e dados precisos para auxiliar na tomada de decisões estratégicas.
O ITIL na Era da Transformação Digital
Na era da transformação digital, o ITIL se torna ainda mais relevante. A adoção de tecnologias como computação em nuvem e inteligência artificial exige uma abordagem flexível e adaptável para o gerenciamento de serviços de TI. O ITIL 4 oferece as ferramentas e orientações necessárias para que as organizações possam aproveitar ao máximo essas tecnologias e garantir o sucesso de suas iniciativas de transformação digital.
Se você gostou deste artigo, fique à vontade para compartilhar este conteúdo nas redes sociais.
Para falar com um de nossos especialistas, clique aqui, e entenda como a 4MATT pode lhe auxiliar a implantar o framework ITIL na sua gestão de ativos.